Mechanical pipe fittings are an essential part of any piping system, allowing for the connection and control of fluid flow in various applications. There are several types of mechanical pipe fittings available, each with its unique characteristics and uses. In this article, we will provide an overview of the different types of mechanical pipe fittings and their applications.
Types of Mechanical Pipe Fittings
There are several types of mechanical pipe fittings available, including:
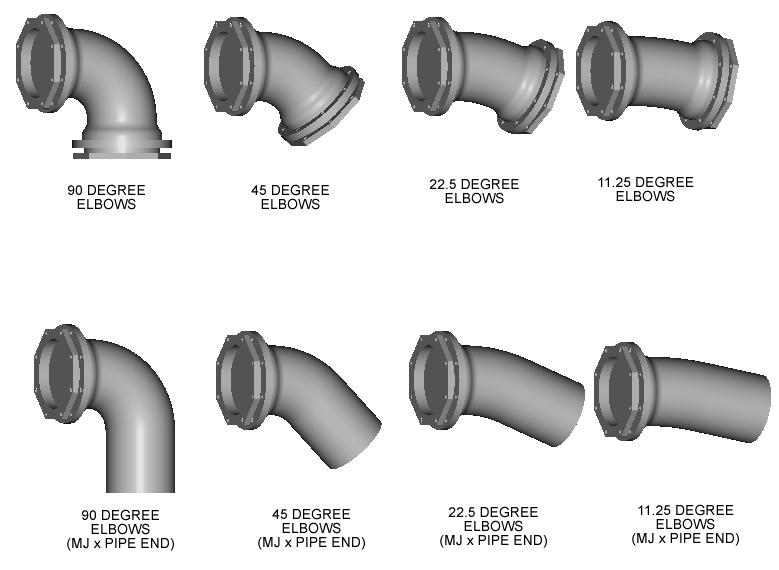
- Elbows: Elbows are used to change the direction of a pipe by 90 degrees or 45 degrees. They are available in various materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and PVC.
- Tees: Tees are used to connect two pipes at a 90-degree angle. They are available in various materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and PVC.
- Couplings: Couplings are used to connect two pipes. They are available in various materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and PVC.
- Unions: Unions are used to connect two pipes, allowing for easy disconnection and reassembly. They are available in various materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and PVC.
- Flexible fittings: Flexible fittings are used to connect pipes in applications where there may be movement or vibration. They are available in various materials, such as rubber and PVC.
- Quick-disconnect fittings: Quick-disconnect fittings are used to connect pipes quickly and easily, without the need for tools. They are available in various materials, such as stainless steel and PVC.
- Compression fittings: Compression fittings are used to connect pipes by compressing the pipe onto a fitting. They are available in various materials, such as copper and PVC.
- Flared tube fittings: Flared tube fittings are used to connect tubes in applications where a flared tube is required. They are available in various materials, such as stainless steel and copper.

Applications of Mechanical Pipe Fittings
Mechanical pipe fittings have a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
- Plumbing: Mechanical pipe fittings are used in plumbing applications to connect pipes and control fluid flow.
- HVAC: Mechanical pipe fittings are used in HVAC applications to connect pipes and control fluid flow in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Industrial: Mechanical pipe fittings are used in industrial applications to connect pipes and control fluid flow in various manufacturing processes.
- Medical: Mechanical pipe fittings are used in medical applications to connect pipes and control fluid flow in various medical devices and equipment.
- Automotive: Mechanical pipe fittings are used in automotive applications to connect pipes and control fluid flow in various vehicle systems.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mechanical Pipe Fittings
When choosing mechanical pipe fittings, there are several factors to consider, including:
- Material: The material of the fitting should match the material of the pipe it will be connecting.
- Size: The fitting should be the correct size to fit the pipe it will be connecting.
- Pressure rating: The fitting should be able to handle the pressure of the fluid flowing through the pipe.
- Temperature rating: The fitting should be able to handle the temperature of the fluid flowing through the pipe.
- Connection type: The fitting should have the correct connection type to connect to the pipe, such as threaded, welded, or push-fit.
- Cost: The fitting should be affordable and provide good value for the cost.
- Quality: The fitting should be of high quality and durable to ensure a long lifespan.
Conclusion
Mechanical pipe fittings are an essential part of any piping system, allowing for the connection and control of fluid flow in various applications. There are several types of mechanical pipe fittings available, each with its unique characteristics and uses. When choosing mechanical pipe fittings.
Comments